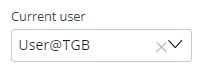
Fields
Pega Platform™ applications collect and process important Case data. By defining the fields that are displayed at runtime, you can collect information from users or present Case information for review. For example, when providing search criteria to book accommodations, users enter each search criteria in a separate field. The criteria return results that are displayed as read-only information.
Each field is a named, reusable UI component. Each field stores a unique value that is associated with a Case. The combination of the field name and the stored value defines a data element in a Case. For example, a field named Metro area and a value of Boston would make up one data element.
When you create a field, you also assign a Field Type. The Field Type identifies the type of information that is stored in the system. By assigning a Field Type, you ensure that users provide valid information in the field and that the system displays data in the correct format.
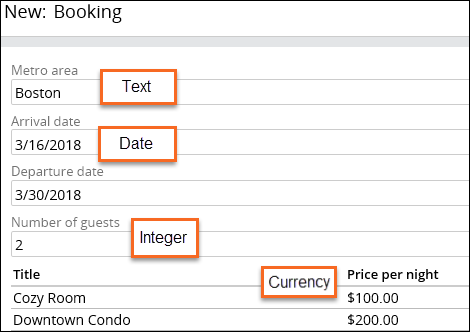
For example, a field named Metro area would be assigned a Field Type of Text and store the value Boston, as shown in the following Booking form:
When creating a field, Pega Platform predicts the Field Type. By default, the Field Type is Text (single line). In the example below, when you name the field Arrival date, the system detects date in the name and sets the Field Type to Date only.
Tip: Verify your Field Type is correct before clicking Submit.
Check your knowledge with the following interaction:
Simple Field Types
In Pega Platform, you can assign a simple Field Type to a field.
Note: The system uses the name of the field to predict the Field Type. When creating a field, make sure to always verify the Field Type by clicking or tabbing to the Field Type list before clicking Submit.
The following table shows a list of simple Field Types and the information each type stores:
| Field Type | Type of Data | Field Example |
|---|---|---|
| Text (single-line) | Any single line of text. |
|
| Text (paragraph) | A large text box that accepts multiple lines of text. |
|
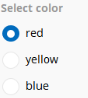
| Boolean | Allows users to select a check box to indicate one of two possible responses. |
|
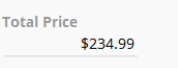
| Currency | Currency symbols and value are stored based on the default currency type. |
|
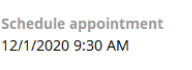
| Date & time | UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) value normalized to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Date automatically displays in a localized format. |
|
| Date only | Calendar date with a localized format. |
|
| Decimal | Numbers with a fractional component. Use this Field Type when fractions are needed. |
|
| Valid email format with an @ symbol. An email field is an action-oriented control, meaning the value stored in the field is displayed as a link. For an email, the link initiates users' default email application. |
|
|
| Integer | Positive and negative whole numbers, including the value zero (0). |
|
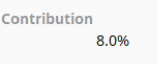
| Percentage | Positive and negative decimal numbers entered as a decimal and displayed as a percentage. For example, .5 displays as 50%. |
|
| Phone | Digits display in a localized format. A phone field is an action-oriented control, meaning the value stored in the field displays as a link. For example, if users access the application on a mobile device, the phone number link initiates a phone call. |
|
| Picklist | A list of predefined values. |
|
| Time only | UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) value normalized to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). |
|
| URL | Web address. A URL field is an action-oriented control, meaning the value stored in the field displays as a link. For a URL, the link initiates the user's default browser and opens the target web page. |
|
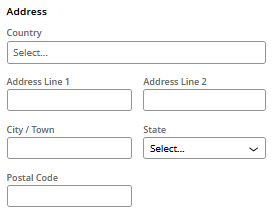
| Address | A region-specific address format. The UI displays the Country field as a dropdown list. Depending on that selection, the UI displays a set of country-specific fields. |
|
| User reference |
Enter or select a user ID that exists in the system. The drop-down or search field shows a list of every operator mapped to the current application rule. |
|
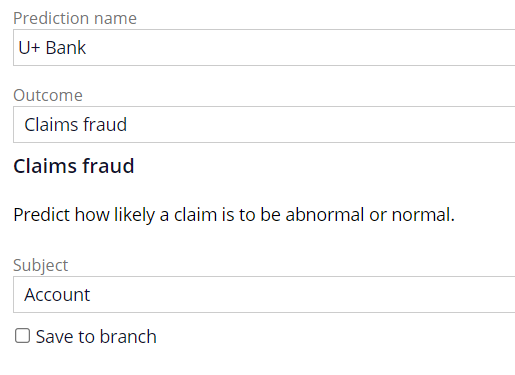
| Prediction |
Optimize the way the application handles work by predicting various outcomes. Predictions can be used to enhance any Step of a Case that uses a condition. Note: Ensure that decision nodes are present in your system. For more information about installing Pega Process AI™, see Installation.
|
|
Tip: An integer field stores only the value that begins at the first non-zero digit. For values that do not require arithmetic calculations, use a text Field Type.
Fancy Field Types
You can also add more complicated Field Types, such as fancy fields. Users can add an address, and the system responds by displaying a map. The system can also display controls to attach a document or display a field to enter or select an existing user ID. The following table shows a list of fancy Field Types and the information each type stores:
| Field Type | Type of data | Example |
|---|---|---|
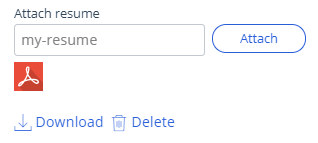
| Attachment | Documents or files. |
|
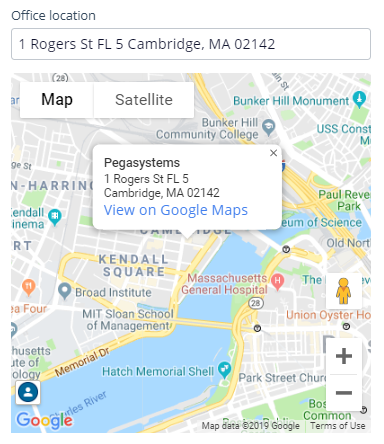
| Location | Address input or automatic geolocation. |
|
Primary fields
Primary fields are the fields that are the most relevant to a Case Type. Designate fields as Primary Fields from the case type data model or the data object. The Case Type data model automatically designates the Label and Description fields as primary by default.
Primary fields are automatically displayed on the Create, Edit, and Details views, which reduces the need for additional UI configuration.
Note: Primary fields are only available in the view-based Constellation architecture. For more information about Primary Field, see Configuring Primary Fields.
Check your knowledge with the following interaction:
This Topic is available in the following Module:
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
Want to help us improve this content?