Volume constraints
What is volume constraint?
In Pega Customer Decision Hub™ you can limit the volume of actions delivered to customers via always-on outbound.
Volume constraints can be set at an action, channel, and/or property level.
Action constraint: It limits the volume of actions that can be sent to customers.
An action constraint is useful in a situation where you have a limited number of offers that you can send to customers, for example, 500 gift vouchers. Configuring an action constraint would ensure that you do not offer more offers than are available.
Channel constraint: It limits the volume of actions that can be delivered via a certain channel.
You can use channel constraint for channel capacity planning. For example, assume that you have a limited call handling capacity in your inbound call center, for example 1000 calls/day. When you send 50,000 emails on a day on a certain regulatory update, let’s say you expect 2%-3% follow-up calls a day from your customers to your contact center, which is about 1000-1500 calls. So, you need to limit the outbound email volume to 35,000 emails a day to match the inbound call center capacity.
Property constraint: By default, actions are grouped under the issue / group business hierarchy. Using a property constraint, you can limit the volume of a set of actions across different issues and groups by grouping them using a property value.
For example, you can group all credit card offers by setting a property, CreditCardType, to VISA. Then you can define a constraint to limit the action volume where CreditCardType is VISA.
Volume constraint modes
Within a volume constraint, the combination of constraints can be defined for one or more actions with one or more channel types.
In situations where a customer is eligible for multiple actions, volume constraint can be applied in two different ways depending on the business requirement. That is, you may specify whether volume constraints should be applied to the actions as a group, or whether each action should be evaluated separately.
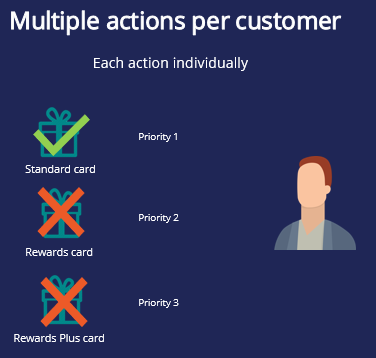
When volume constraint is evaluated separately, each action is checked for the customer separately against applicable channel and action constraints. A customer receives only one action, the one with the top priority, even though the limits for the other low priority actions, are not reached.The top action is selected based on factors like propensity, action value and business levers defined in Next-Best-Action Designer Arbitration.
For example, let’s consider that a customer is eligible for Standard card, Rewards card, and Rewards Plus card credit card actions and Standard card is the top priority card. Also, assume that the remaining volume for all three actions are above zero. When you set volume constraints to check each action, the customer will be presented only with the top priority action, Standard card.
When volume constraint is applied for actions as a group, the highest priority action is selected to apply constraints on the channels and actions, without removing the other actions for a customer. That is, a customer receives all the actions he/she qualifies for, provided that the limit for the top priority action is not reached. The other low priority actions are selected even though the limits for those actions are reached.
For example, let’s consider that a customer is eligible for Standard card, Rewards card, and Rewards Plus card actions and Standard card is the top priority action. Also, the remaining volume for Standard card is above zero, but for the other two actions it has reached zero. When you set volume constraints to check actions as a group, the customer receives all the actions.
Evaluating actions as a group allows Pega Customer Decision Hub to present all eligible actions to a customer.
This Topic is available in the following Module:
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
Want to help us improve this content?