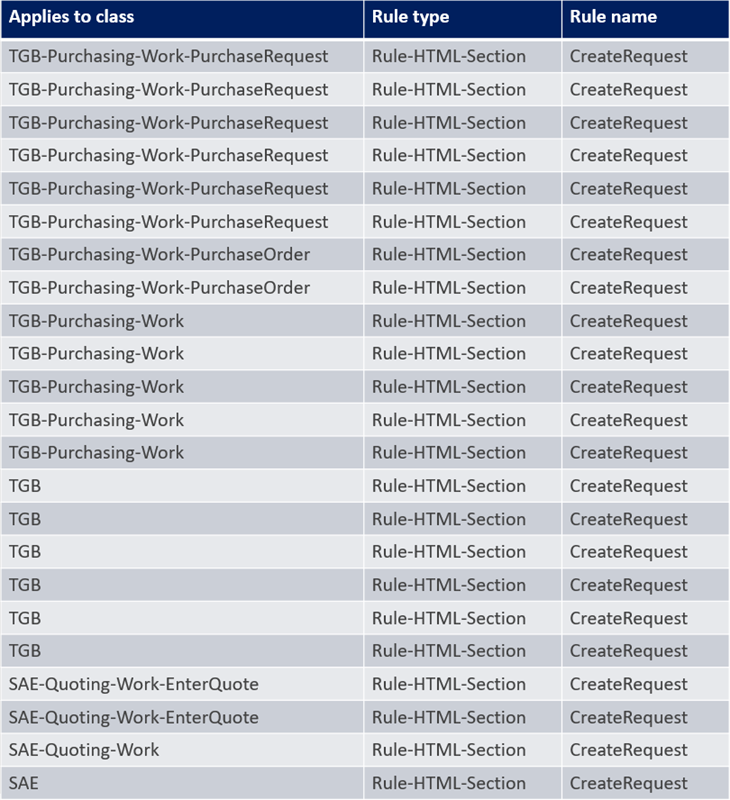
Filtrado de reglas por propósito
The purpose of a rule is defined by the combination of the rule name and rule type. The first step of the rule resolution algorithm creates a list of all rules that match the referenced rule's purpose. In the example, all HTML section rules named CreateRequest are assumed to have the same purpose, and the rule resolution algorithm collects the rule instances into the list.
There can be many instances of the rule in the initial list of rule candidates because each rule instance has a different ruleset and ruleset version.
Nota: The applies to class is displayed in this list to help provide context where each instance of the rule in question is found. The ruleset and ruleset version are omitted from this list.
Rules marked Not Available
In this step, the rule resolution algorithm filters the list of rule candidates and removes any rules where the rule Availability is set to Not Available.
In the example, the rule resolution algorithm finds three rules where the rule Availability is set to Not Available. The rules are removed from the list of rule candidates.
In the center of the following image, slide the vertical line to view the three rules highlighted on the left and the same three rules removed from the list on the right.
Rules in inapplicable rulesets
In this step, the rule resolution algorithm uses the operator's Ruleset list to determine which candidate rules the operator can access.
Tip: The Ruleset list is a combination of the ruleset name and a Major-Minor version number.
Each rule candidate must belong to a ruleset listed in the operator's ruleset list to be included in the results. Each rule must have the same major version number and a minor version number less than or equal to the specified Minor version number listed in the operator's ruleset list.
In the example, assume the operator's ruleset list includes Purchasing:02-01 and TGB:03-01. The three rules in the Purchasing:01-01-01 ruleset are eliminated because they do not match the major version defined in the operator's ruleset list (Purchasing:02-01).
In the center of the following image, slide the vertical line to view the three rules highlighted on the left and the same three rules removed from the list on the right.
The rule in the Purchasing:02-02-01 ruleset is also eliminated because the minor version number (Purchasing:02-02) is higher than the minor version number defined in the operator's ruleset list (Purchasing:02-01).
In the center of the following image, slide the vertical line to view the highlighted rule on the left and the same rule removed from the list on the right.
De las reglas que figuran en los rulesets de TGB, solo una regla coincide con el número de versión principal mayor que figura en la lista de rulesets del operador (TGB:03-01). Todas las demás reglas en los rulesets de TGB se eliminan.
En el centro de la siguiente imagen, deslice la barra vertical para ver las reglas resaltadas a la izquierda y las mismas reglas eliminadas de la lista a la derecha.
Las reglas que figuran en los rulesets Quoting y SAE se eliminan porque los rulesets no figuran en la lista de rulesets del operador.
En el centro de la siguiente imagen, deslice la barra vertical para ver las reglas resaltadas a la izquierda y las mismas reglas eliminadas de la lista a la derecha.
Reglas fuera de la jerarquía de clase
En este paso, el algoritmo de resolución de reglas examina la clase applies to class (Aplica a) en la lista de reglas candidatas si las reglas candidatas restantes están dentro de la jerarquía de herencia de la regla referenciada.
Caution: Para ser considerado en este paso, un tipo de regla debe tener seleccionado el checkbox Use class-based inheritance to arrive at the correct rule to execute? (¿Usar herencia basada en clase para determinar la regla correcta para ejecutar?) en la definición de clase.
La clase Aplica a de las reglas candidatas restantes debe coincidir con el árbol antecesor de la regla referenciada para incluirse en los resultados. Solo se conservan en la lista las reglas que se encuentran en el árbol antecesor de la regla referenciada, ya sea por patrón o por herencia directa.
Nota: El árbol antecesor hace referencia a la herencia de la regla.
En el ejemplo, la regla referenciada aplica a la clase TGB-Purchasing-Work-PurchaseRequest. Hay una regla candidata que no está en el árbol antecesor, por lo que se elimina de la lista.
En el centro de la siguiente imagen, deslice la barra vertical para ver la regla resaltada a la izquierda y la misma regla eliminada de la lista a la derecha.
Compruebe sus conocimientos con la siguiente actividad:
This Topic is available in the following Module:
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
¿Quiere ayudarnos a mejorar este contenido?
