AI versus robotic automation
Artificial intelligence and robotic automation comparison
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotic automation are similar in that they perform a task or tasks instead of a human being. AI and robotic automation solutions are not impacted by geography and are not prone to error, like human beings. However, the application of each technology differs based on what you are trying to achieve. You could also design a solution that uses AI and robotic automation capabilities in tandem; they are not mutually exclusive technologies. Grasping the benefits and differences between AI and robotic automation allows you to identify opportunities to use these technologies and to design an application that can radically change the way the organization performs work. Pega offers the following technology to meet these needs:
- AI capabilities, in the form of the Intelligent Virtual Assistant, Customer Decision Hub, the Decision Management features
- Robotic automation capabilities, including Robotic Desktop Automation (RDA), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and Workforce Intelligence (WFI)
The following table summarizes the key differences between Robotic Desktop Automation (RDA), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Workforce Intelligence (WFI), and AI capabilities.
| Capability | RDA | RPA | WFI | AI |
| Assists end users with routine manual tasks | X | |||
| Fully replaces the end user's involvement in the task | X | X | ||
| Identifies opportunities for process improvement | X | |||
| Self learning technology, requiring no programming | X |
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be defined as anything that makes the system seem smart. An artificial intelligence solution learns from the data available to it. This data can be structured or unstructured (such as big data) and can take in images, sound, or text inputs. The value of AI increases as the solution gains age and experience, not unlike a human being.
For an AI solution to be self-learning, the AI solution uses experiences to form its basis of knowledge, not programmed inputs. The Adaptive Decision Manager (ADM) service is an example of adaptive learning technology. For example, when training an Artificial Intelligence solution to recognize a cat, you do not tell the AI to look for ears, whiskers, a tail, and fur. Instead, you show the AI pictures of cats. When the AI responds with a rabbit, you coach the AI to distinguish a cat from a rabbit. Over time, the AI becomes better at identifying a cat. This technology can be a powerful ally in building a customer's profile, preferences, and attributes.
An AI solution can also predict the next action a customer will take. This ability allows an organization to serve the customer in a far more effective way. The organization can know why a customer is contacting them before the customer even calls. For example, an AI solution can guide a customer service representative to offer products or services that the customer actually wants, based on the previous behavior of the customer. Predictive Analytics provides this capability.
The Customer Decision Hub combines both predictive and adaptive analytics to provide a seamless customer experience and only shows offers relevant to that customer. The Customer Decision Hub is the centerpiece of the Pega Sales Automation, Pega Customer Service, and Pega Marketing applications.
AI uses a natural language processing (NLP) to detect patterns in text or speech to determine the intent or sentiment of the question or statement. For example, a bank customer uses the Facebook messenger channel to check his account balance. In the background, the bank's software analyzes the intent of the question in the message, performs the balance inquiry, and returns the response to the customer. The Intelligent Virtual Assistant is an example of NLP in action.
Note: AI is a powerful tool. AI can also carry risk if you are not cautious. For more information on this topic, see the Responsible AI requires a T-Switch presentation on Pega.com.
Robotic automation
Robotic automation is technology that allows software to replace human activities that are rule-based, manual, and repetitive. Pega robotic automation applies this technology with:
- Robotic desktop automation (RDA)
- Robotic process automation (RPA)
- Workforce intelligence (WFI)
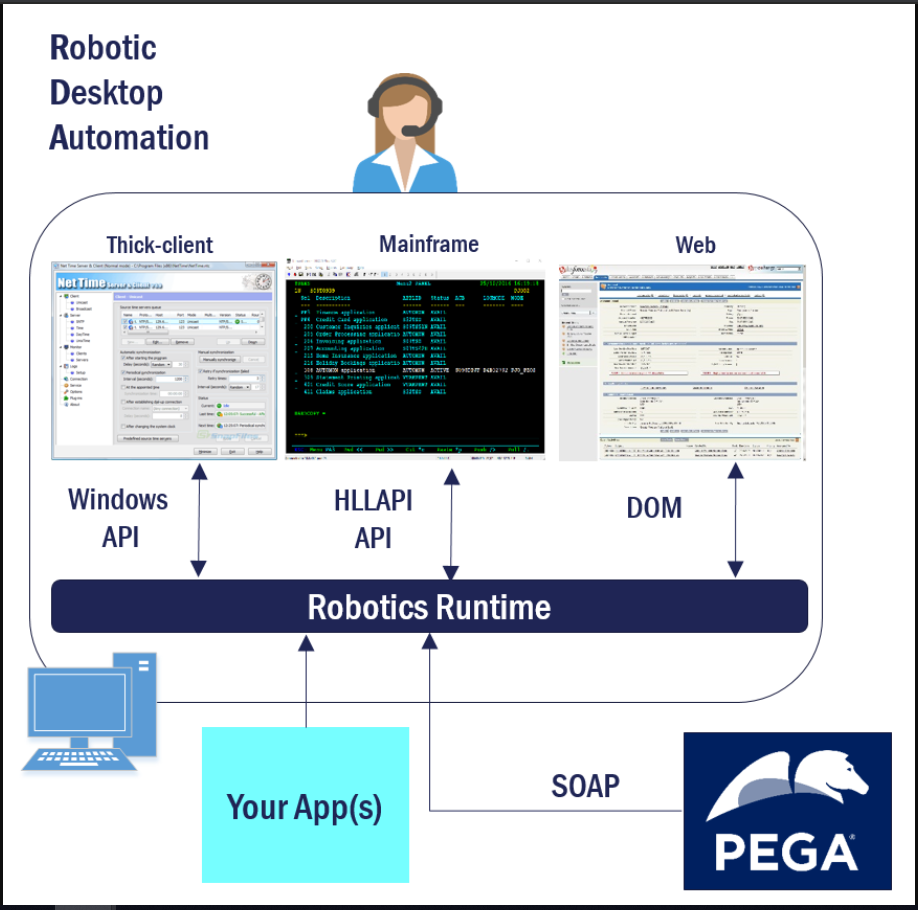
Robotic desktop automation (RDA) automates routine tasks to simplify the employee experience. RDA mimics the actions of a user interacting with another piece of software on the desktop. For example, a customer service representative (CSR) logs into five separate desktop applications to handle customer inquiries throughout the day. You can use RDA to log that CSR into these applications automatically. This allows the CSR to focus on better serving the customer.
Usage of RDA is also known as user-assisted robotics.
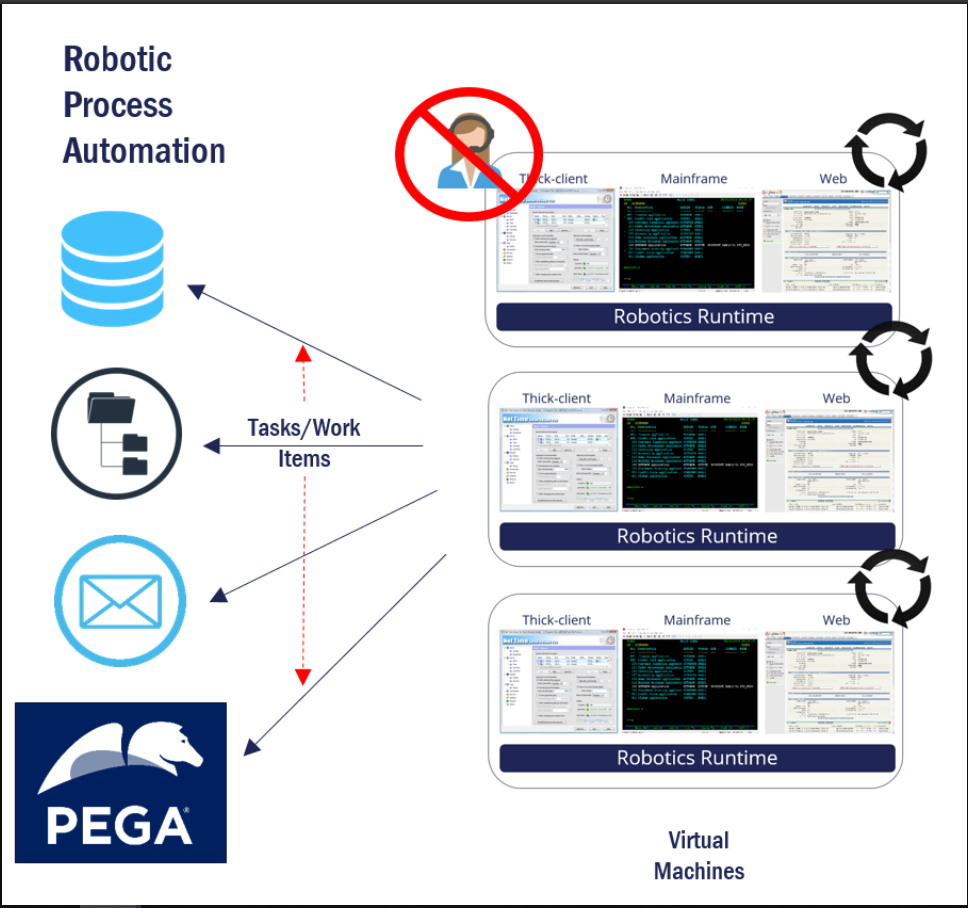
Robotic process automation (RPA) fully automates routine and structured manual processes. No user involvement is required. With RPA, you assign a software robot to perform time-consuming, routine tasks with no interaction with a user. These software robots perform work on one or more virtual servers. For example, a bank requires several pieces of documentation about a new customer before the bank can onboard that new customer. Gathering this information can take one person an entire day to complete this task. You can use RPA to gather these documents from one or more source systems. The software robot can perform the same process in minutes.
The use of RPA is also known as unattended robotics.
Workforce intelligence (WFI) connects desktop activity monitoring to cloud-based analytics to gain insight about your people, processes, and technology. WFI enables the organization to find opportunities to streamline processes or user behavior. For example, this technology can identify where a user is repeatedly copying and pasting, switching screens, or typing the same information over and over. This allows the organization to detect areas for process improvement. When you implement changes to those processes, the organization can realize significant time and money savings.
For more information on RDA, RPA, and WFI, see the Pega Robotic Automation landing page on the Pega Community.
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
Want to help us improve this content?