Business use case: Cross-sell on the web
Introduction
Pega Customer Decision Hub's Next-Best-Action Designer lets you configure how you want the always-on brain to select the best offer for a customer. The best offer is the result of a series of decisions that are executed in a hierarchical fashion by the brain. Cross-selling on the web channel will help you improve 1-to-1 customer engagement, drive sales, and deliver Next-Best-Actions in real-time.
Video
Transcript
This video describes a typical cross-selling use case on the web channel.
U+ is a retail bank. The bank would like to leverage its website as a marketing channel to improve 1-to-1 customer engagement, drive sales, and deliver Next-Best-Actions in real-time.
The bank has decided to use the Pega Customer Decision Hub™ to recommend more relevant banner ads to its customers when they visit their personal portal.
Banner ads are shown on various pages throughout the website.
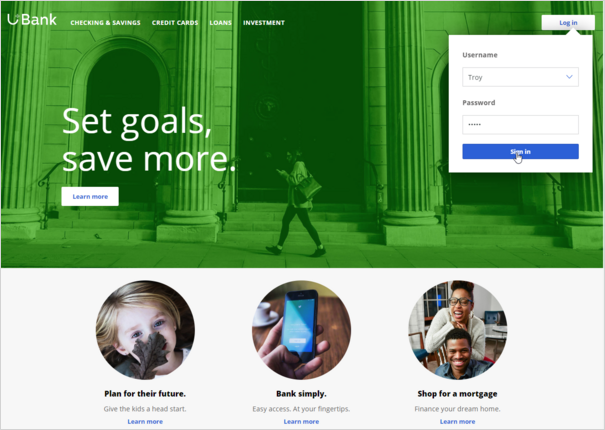
For example, on the home page, U+ can display a Hero banner at the top of the page, which is typically a larger image with bigger typeface.
Below that, there is space to display several Tile banners, which are typically smaller.
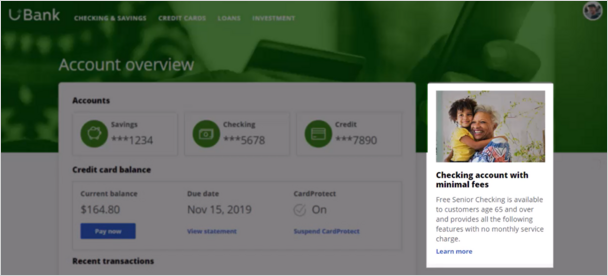
When customers log in to their personal portal, they also see a Tile banner on the 'Account overview' page.
The main intent of U+ at this stage is to increase their web engagement. This can be measured by click-through rate. A Click-through is recorded when the customer clicks on the 'Learn more' link.
The bank would like to use these banners on the 'Account overview' page, to display offers that are more relevant and likely to receive a positive response.
The offers will be selected by a combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and other business rules. The AI and business rules are defined in the Pega Customer Decision Hub.
The Pega Customer Decision Hub is the always-on customer brain that acts as a single, centralized decision authority. The always-on customer brain selects the right offer to be displayed to each customer who visits the bank's website.
Next-Best-Action Designer lets you configure how you want the always-on brain to select the best offer for a customer. The best offer is the result of a series of decisions that are executed in a hierarchical fashion by the brain.
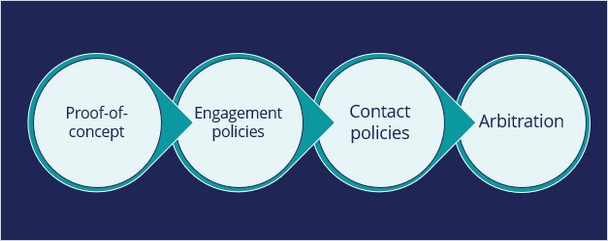
The bank plans to implement the requirement in multiple phases.
The first phase is a proof-of-concept phase. In this phase, the goal is to display a credit card offer on the U+ website. This requires getting the basic environment up and running, setting up the business structure, defining an Action and a Treatment, and enabling channels and triggers for Next-Best-Action.
As a result of this phase, a credit card offer will be displayed on the 'Account overview' page to all customers who visit the U+ web site. For example, if customer Troy logs in to his account, the 'Cash back' offer is displayed. If another user logs in, they will see the same offer. However, in practice, more offers should be displayed. Also, not all offers may be available to a customer for various reasons.
The next phase is to add customer engagement policies. Engagement policies are the set of conditions such as eligibility, applicability, and suitability that qualify an offer, or a group of offers for a customer. As a result of engagement rules, customers will see only those offers that the organization believes they should be exposed to. For example, Troy logs in, he sees the Rewards Card, but for Barbara this is not applicable, so it will never appear; instead, she sees the Rewards Plus Card.
Too many contact attempts over a short period of time can have a negative impact on a customer's attitude toward further offers by your company. Therefore, in the next phase, U+ implements some contact policies using suppression rules, which allow an offer to be put on hold after a specific number of outcomes. For example, if Troy ignores an ad a few times, then the ad will no longer be shown to him over a period of time. Instead, his 'Account overview' page will show a different ad.
Basically, from a set of all available offers, the choice is narrowed down by engagement policies. Then the selection is further narrowed down by suppression rules.
After the engagement policies and suppression rules have "whittled down" the total possible offers to a few, Arbitration is used to choose the top offer based on what is relevant for the customer right NOW.
Arbitration is the last phase of cross-sell in the U+ web use case.
Arbitration aims at balancing customer relevance with business priorities. Specifically, Propensity, Context Weighting, Business Value, and Business Levers are given numerical values. A simple formula is then used to arrive at a prioritization value, which is used to select the top offer. For example, Troy qualifies for three credit card offers. When he logs in, he sees the top offer for him, the Standard Card. This offer is the Top 1 because the priority value is the highest among all other offers.
This video has concluded. It showed you a typical cross-selling use case on the web channel and its four phases of implementation.
This Topic is available in the following Modules:
If you are having problems with your training, please review the Pega Academy Support FAQs.
Want to help us improve this content?